A significant congressional committee in the US approved President Donald Trump’s new tax cut bill on Sunday, which is expected to pass the House of Representatives later this week.
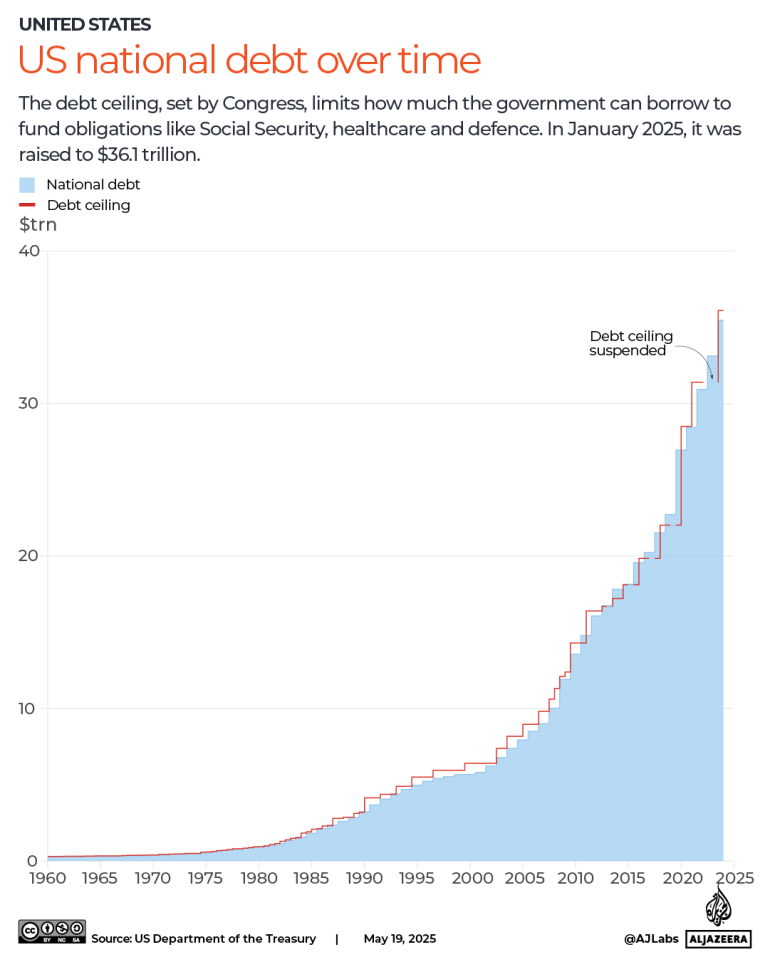
The bill extends Trump’s tax cuts from 2017 and could raise the country’s debt by $5 trillion, raising questions following Moody’s’ recent downgrad of US credit ratings on Friday, which raised concerns about the country’s growing $36 trillion debt.
The US is grappling with growing concerns about its long-term fiscal stability, which is the highest level of the world.
How much debt is US?
Debt is simply the total amount of money that the US government currently owes its creditors, totaling $ 36. 2 trillion. This accounts for 122 percent of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP) annually, and it is expanding by about $1 trillion every three months.
During the pandemic in 2020, the ratio reached 133 percent, which was the highest debt-to-GDP ratio. The US has the highest debt-to-GDP ratio among the top ten nations in the world.
Why does the debt ceiling keep rising, and what is it?
The government runs a deficit when it spends more money than it collects.
The government takes more money out to pay this deficit. The US Congress establishes a maximum amount of money that the government can borrow to pay off existing obligations like Social Security, healthcare, and defense in order to ensure that borrowing is approved by the legislature. The debt ceiling refers to this cap.
If the cap is not raised or suspended by Congress, the government is unable to borrow more once it has been exceeded. Congress has 78 times raised, suspended, or changed the debt ceiling to allow for more borrowing from the US.
Under various presidents, the federal deficit increased.
The government spends more money than it spends in a single year, or in terms of the federal deficit. A surplus in the federal government would indicate that the US is spending more money than it is bringing in.
During Trump’s first term, the deficit increased sharply, particularly in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, during which the government spent a lot while job losses caused tax revenues to decline. The deficit accounted for nearly 15% of the GDP in that year.
There was a federal surplus under former president Bill Clinton as a result of favorable economic conditions, such as the dot-com boom, as well as tax increases that generated higher income.

Treasury bills, notes, and bonds: what are they?
The Treasury, the federal government’s finance division, is the place where the US goes when it needs to borrow money.
The Treasury sells a variety of debt instruments to investors, including Treasury bills, Treasury notes, and Treasury bonds, for borrowing money.
The US government receives these loans in the form of loans, which are essentially promises to repay them with interest.
Because of the low risk of the US failing to pay its investors, US Treasuries have long been regarded as a safe asset.
Different debt securities have different maturities, and the investor receives a refund for the debt.
- Treasury bills (T-bills) are short-term and expire in a year.
- Treasury notes (T-notes) are medium-term and mature for between two and ten years.
- Treasury bonds (T-bonds) have a 20 to 30 year maturity.

Who is a US debtor?
About $27.2 trillion of the US debt, or 35%, is held domestically, out of which:
- US private investors and organizations own $ 15.16 trillion (42%), the majority of which are in the form of savings bonds, mutual funds, and pension funds.
- US intra-governmental organizations and trusts hold $ 7.36 trillion (20%) of that amount.
- The Federal Reserve holds $4.63 trillion (13%) in its hands.
The largest non-government holder of US Treasury bills, worth $314 billion, is Warren Buffett, who owns the majority of the money among individuals.
The remaining quarter’s worth, which is $2.05 trillion (25%), is held by foreign investors.
Over the past 50 years, foreign companies have increased their stake in US debt by fivefold. Only 5% of foreign investors owned the company in 1970, up from 25% today.

Which nations are the most indebted abroad?
Countries purchase US debt because it facilitates exchange rate control, provides stability, and guarantees interest income. It also provides a safe, stable investment for their foreign currency reserves.
Foreign investors currently have debt totaling $9.05 trillion:
- $ 1.13 trillion is held by Japan.
- The United Kingdom holds $779.3 billion, making it the second-largest non-US treasury holder since March.
- China holds $765.4bn
- Because it is a tax haven, the Cayman Islands ($455.3 billion) are a significant source of US debt.
- Canada ($426.2bn)
In trade negotiations with the Trump administration, both Japan and China have indicated that they will use their substantial holdings of US Treasury securities as leverage.
Japanese Finance Minister Katsunobu Kato earlier this month stated that trade negotiations could turn to Japan’s massive holding of US treasuries.
China has also been slowly selling US Treasury bills for years. China’s US Treasury holdings dropped to their lowest level since 2009 as a result of efforts to diversify reserves and persistent trade tensions.

What does the typical American’s high US debt mean?
Budgets and public spending can be impacted by the US government’s increasing spending on debt interest repayments as it becomes more expensive to support itself.
Source: Aljazeera
Leave a Reply