EXPLAINER
The mission went much longer than expected.
On June 5, 2024, American astronauts Sunita “Suni” Williams and Barry “Butch” Wilmore boarded the Boeing Starliner Calypso. Eight days on the International Space Station (ISS) was intended for them.
However, the spacecraft’s thrusters malfunctioned as it approached the station, prompting NASA to keep them on the ISS while repairs were being made.
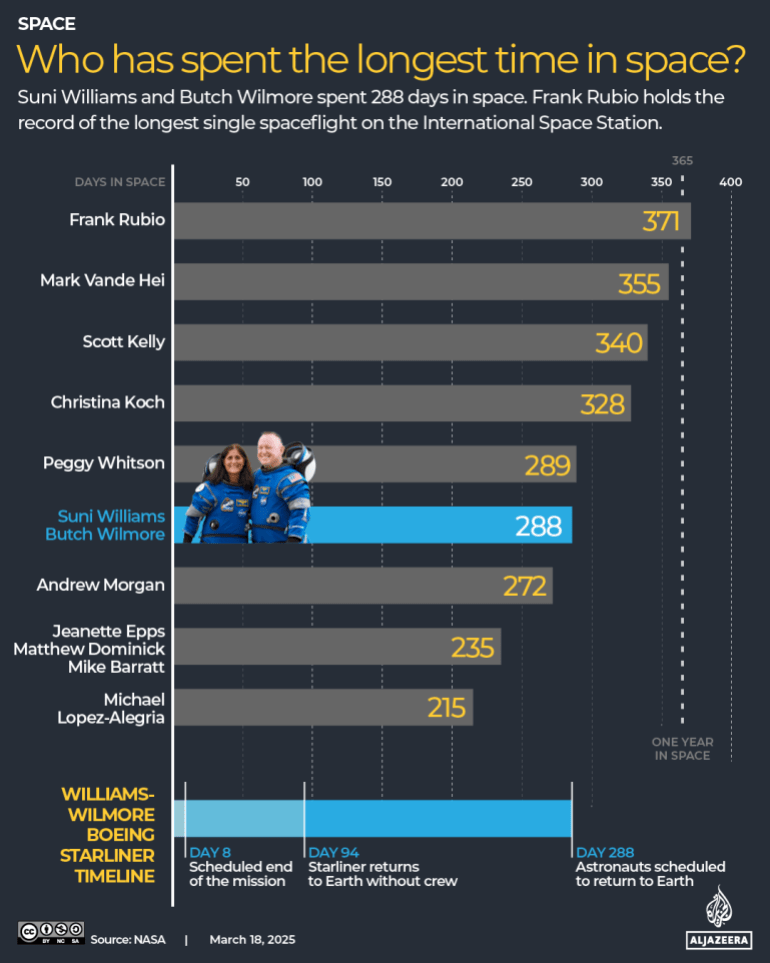
Williams and Wilmore are now two of the longest-serving space travelers on a single mission thanks to their nine-month, 288-day mission.
Who has been in space for the longest?
The ISS travels to Mars on average 225 million kilometers (140 million miles) from Earth at an altitude of 354 kilometers (220 miles).
With more than a year spent on the ISS, astronaut Frank Rubio currently has the longest space mission of all time for NASA.
Valeri Polyakov, a Russian who spent 437 days on board the Mir space station, holds the overall record for a single spaceflight.
The SpaceX Crew-9 mission made its return to Earth when?
Williams and Wilmore’s SpaceX Dragon spacecraft crashed about 5:57 p.m. local time (21:57 GMT), after undoing from the ISS at 5:05 p.m.
Aleksandr Gorbunov, a cosmonaut from Roscosmos, was aboard with Wilmore and Williams.
The lead up to the splashdown was live-streamed by NASA.

The crew will have to adjust both physically and mentally to returning to Earth.
How does physical health suffer from space travel?
The body feels brutally shivering in months of microgravity. Without the gravitational pull of the Earth, muscles and bones would deteriorate.
Because they don’t use their legs to support their weight, astronauts quickly lose muscle mass. They lose 1% of their bone mass each month, which is equivalent to an entire year of Earth ageing due to their fragile bones.
Another major issue is radiation. Despite the magnetosphere shielding the ISS, astronauts on missions lasting six months or longer receive more than ten times the radiation as it would naturally be on Earth. Long-term exposure is linked to higher risk of developing cognitive decline and cancer.

- Body mass and fluids: While in space, astronauts lose about 20% of their body mass and about 5% of it.
- Muscle: Microgravity results in muscle atrophy, but taking supplements and two hours of exercise per day, six days per week can help.
- Skin: In space, skin thins, brittles, and heals more slowly.
- Eyes: Radiation increases the risk of cataracts while microgravity impairs vision.
- DNA: About 7% of genes are still inactive after returning to Earth, compared to the majority of genes.
- Cognitive psychology and radiation: Alzheimer’s may develop and cause brain damage. Motion sickness is caused by space changing orientation.
- Red blood cell production decreases as blood circulation slows down and red blood cell production slows down. Cardiac arrhythmia is a common condition.
- Immune system: It becomes less effective. Six months of space-time radiation exposure equals ten times the annual exposure on Earth.
- Bones: Approximately one-third of the bone mass is lost each month due to bone loss and deformation. Because of their increased spine expansion while in orbit, astronauts gain height.
How does the body repopulate from Earth?
Returning to Earth doesn’t immediately relieve astronauts’ bodies’ months of strain. Balance issues, dizziness, and weakened cardiovascular function are some of the symptoms of their bodies adapting to gravity.
Not everything comes back to normal even after a few months. They are susceptible to degenerative diseases, cancer, and nerve damage over the long term.

- Return of the spine to normal size after entering space. Blood pressure is normalized, and flirtatious behavior is no longer a problem.
- After a week, motion sickness, balance issues, and disorientation are gone. Sleep resumes as usual.
- Two weeks later, body fluids that were lost are recovered and the immune system returns. Red blood cell production returns to normal levels.
- One month later, almost all of the muscle reformation has finished.
- Three months later, the skin has fully developed. Body mass is restored to Earth-levels, and visual issues no longer exist.
- Six months later, there is still a higher risk of bone fractures and cancer. Exactly 7% of genes are still in the disorder, compared to 93 percent of those that are back to normal.
Source: Aljazeera




Leave a Reply